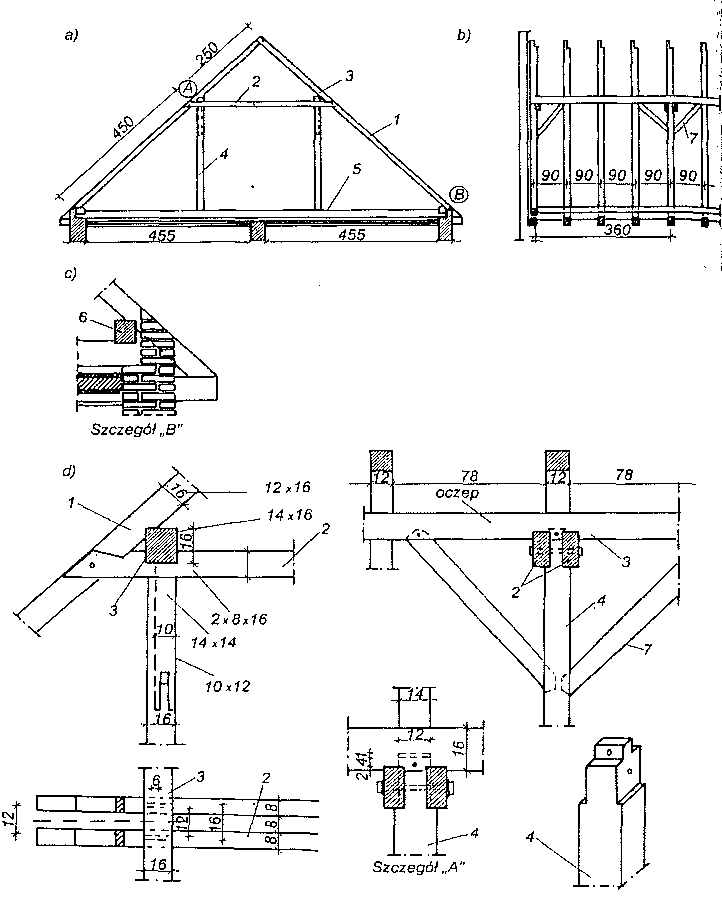
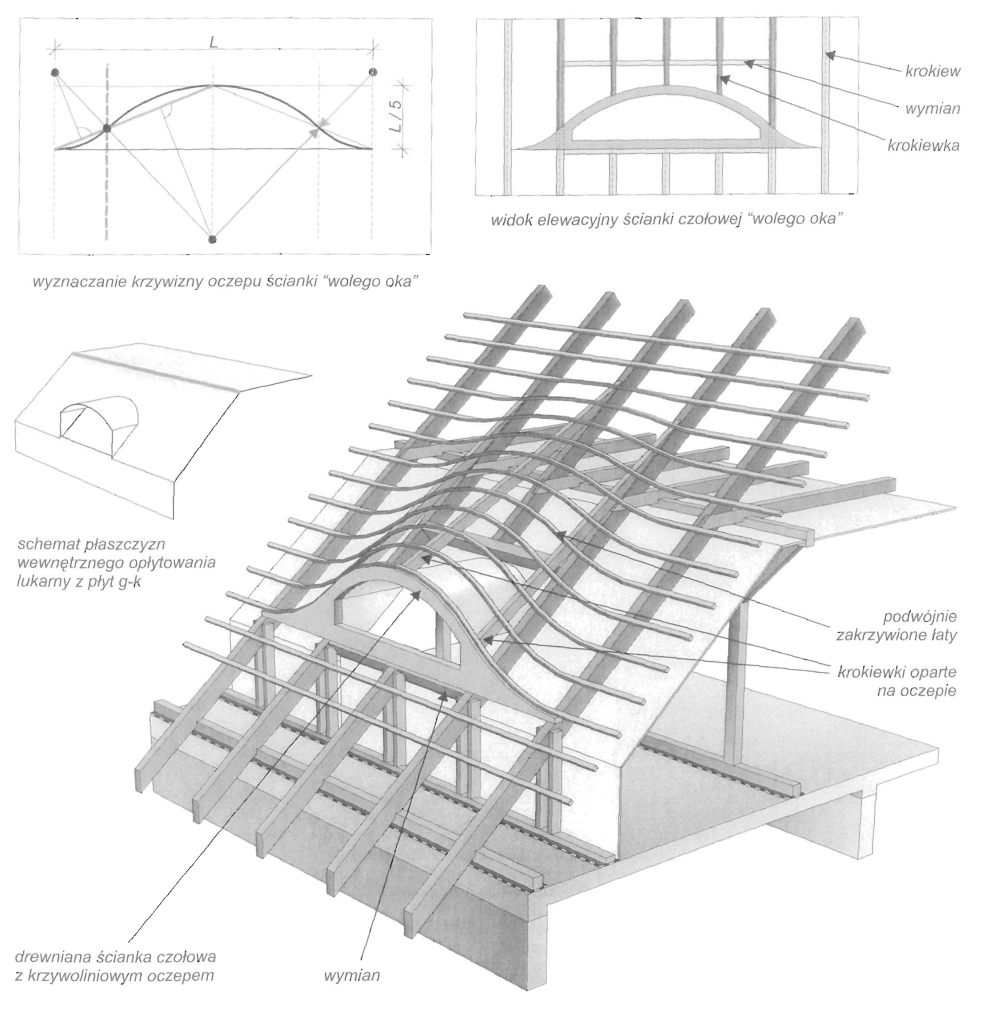
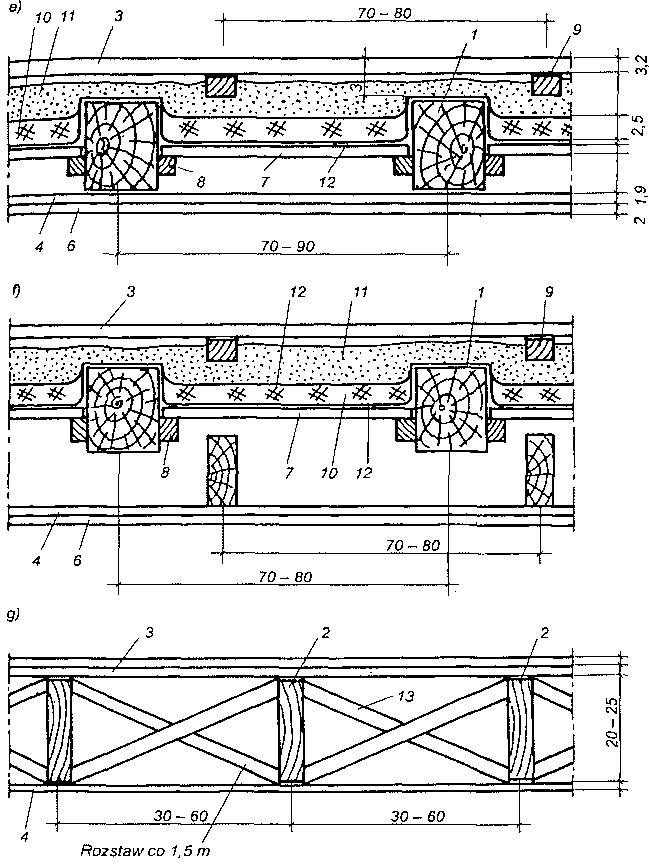
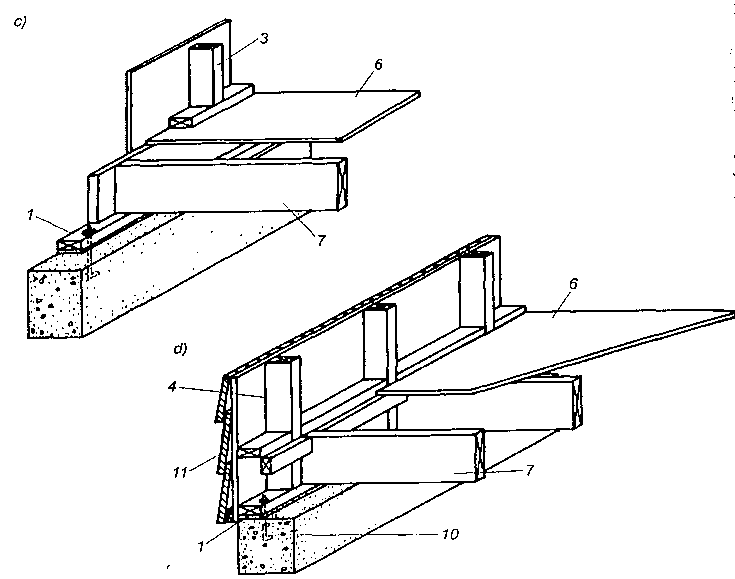
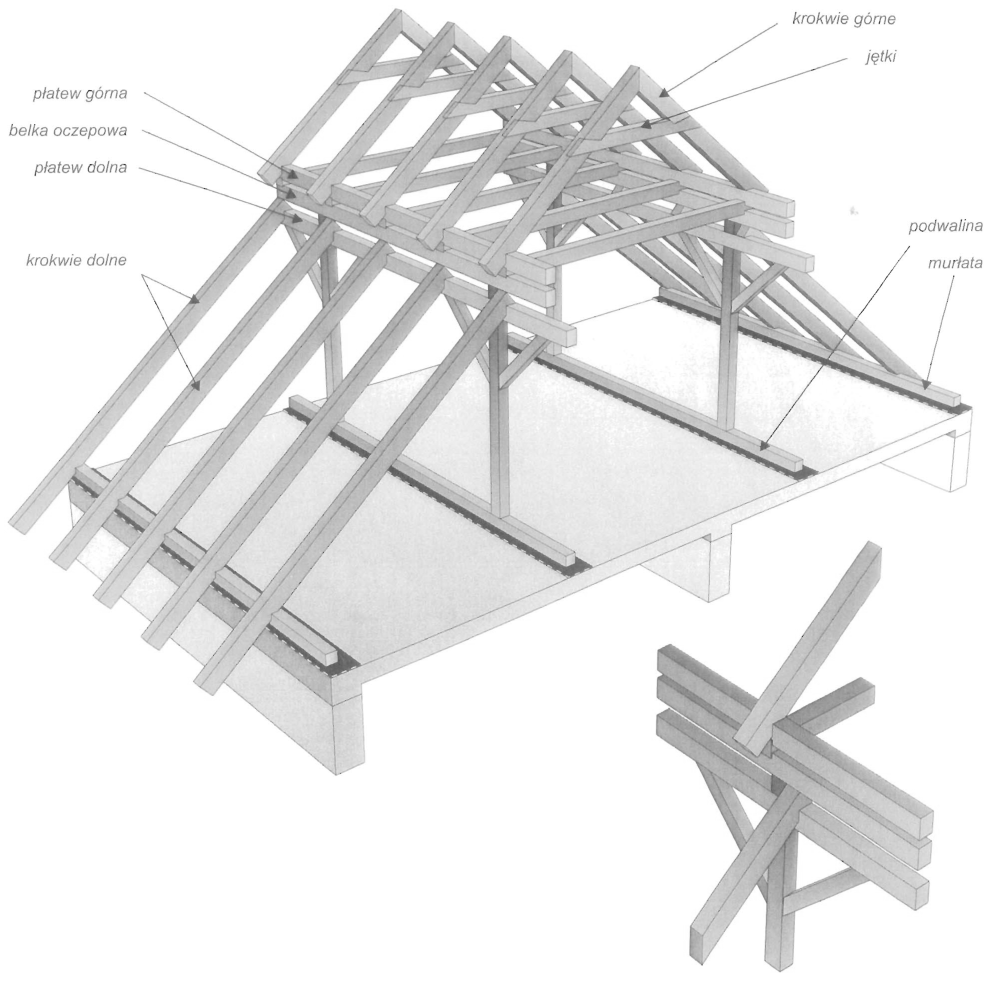
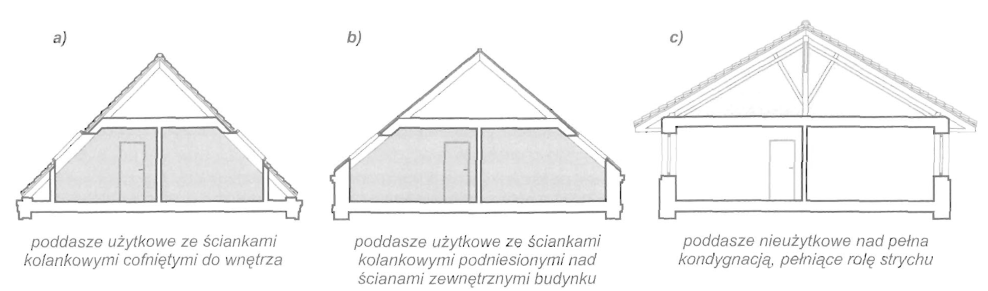
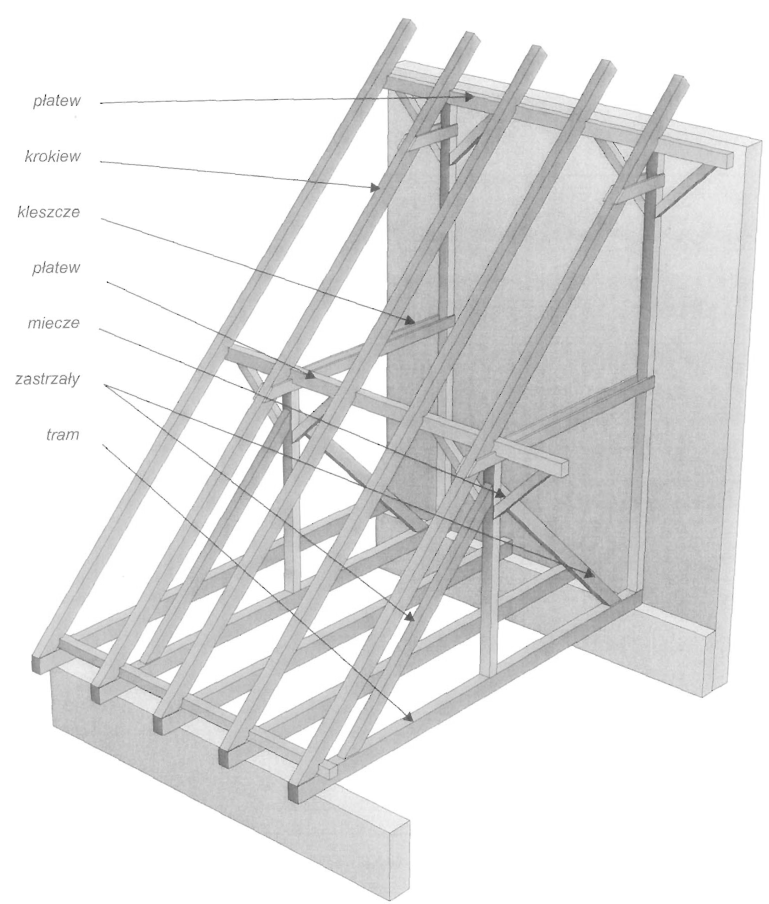
Dach stanowi przekrycie budynku i składa się z konstrukcji nośnej, tzw. więźby dachowej i pokrycia. Głównymi elementami więźby dachowej są wiązary dachowe. Rozróżnia się wiązary pełne ustawione w odstępach ok. 3,0-4,5 m oraz wiązary puste rozstawione między nimi w odstępach ok. 0,8-1,2 m. Do wiązarów przymocowuje się łaty lub deski, które stanowią podkład pokrycia dachowego. Zasadniczymi elementami wiązarów dachowych w zależności od ich konstrukcji, są: krokwie, jętki, kleszcze, stolce, płatwie,zastrzały i belki.
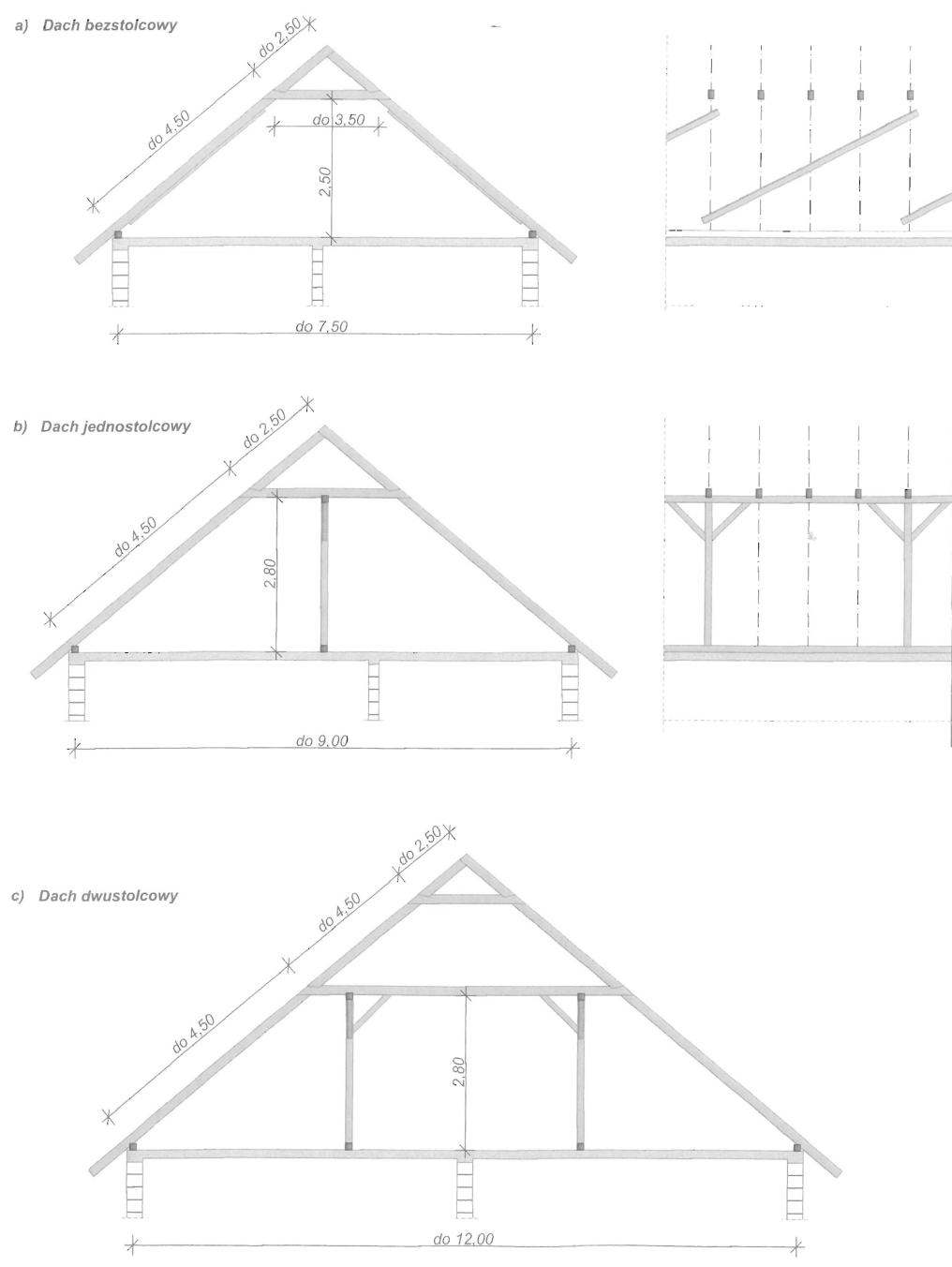
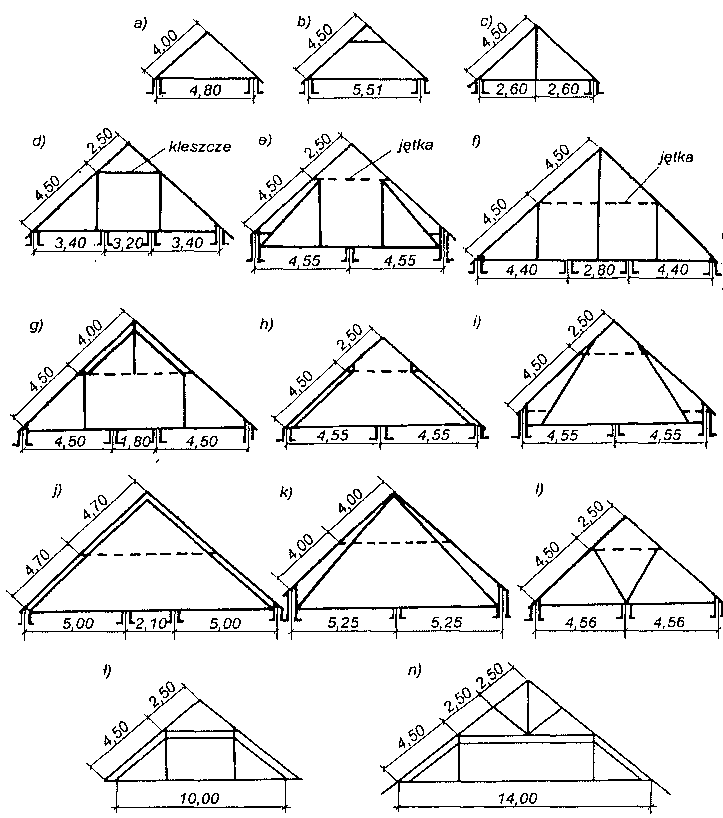 Rodzaje wiązarów dachowych dwuspadowych — dachy: a), b) bezstolcowe, c) ze stolcem pojedynczym, d) jętkowy lub płatwiowo-kleszczowy ze stolcem podwójnym, e) /c stolcem podwójnym i ścianką kolankową, f) ze stolcem potrójnym, g) ze stolcem potrójnym górny stolec zawieszony, h) ze stolcem podwójnym leżącym, i) ze stolcem podwójnym leżącym i ścianką kolankową, j) z krokwiami głównymi, k) z krokwiami głównymi i ścianką kolankową,l) ze stolcem kozłowym, ł), n) o stolcu wiszącym podwójnym.
Rodzaje wiązarów dachowych dwuspadowych — dachy: a), b) bezstolcowe, c) ze stolcem pojedynczym, d) jętkowy lub płatwiowo-kleszczowy ze stolcem podwójnym, e) /c stolcem podwójnym i ścianką kolankową, f) ze stolcem potrójnym, g) ze stolcem potrójnym górny stolec zawieszony, h) ze stolcem podwójnym leżącym, i) ze stolcem podwójnym leżącym i ścianką kolankową, j) z krokwiami głównymi, k) z krokwiami głównymi i ścianką kolankową,l) ze stolcem kozłowym, ł), n) o stolcu wiszącym podwójnym.
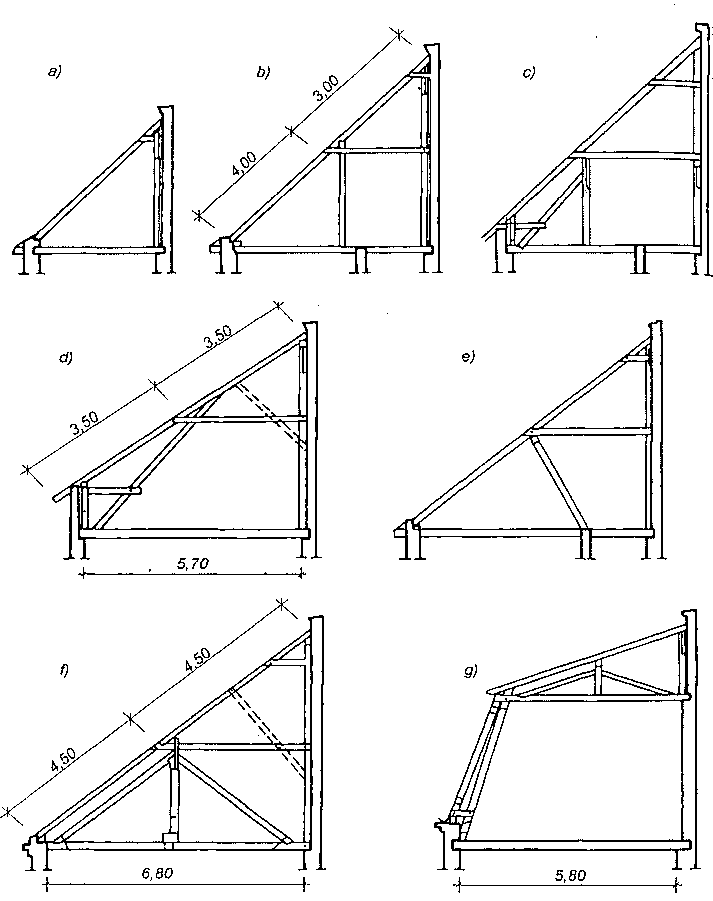
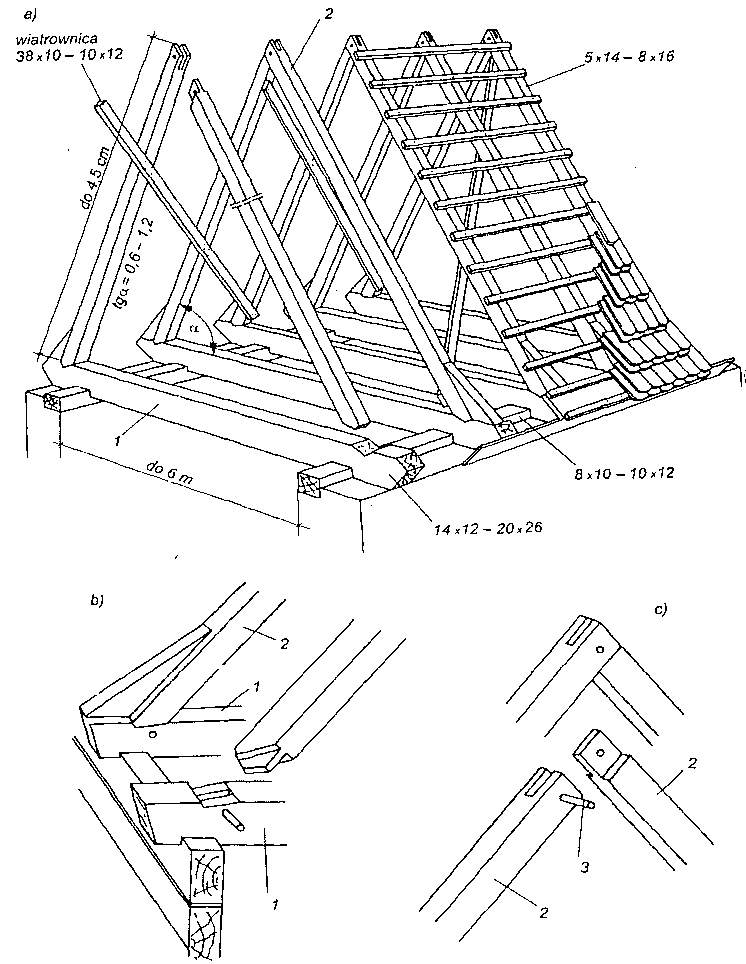
Na rysunku powyżej przedstawiono schematy najczęściej spotykanych wiązarów drewnianych dwuspadowych, które powstały na drodze wielowiekowego ich rozwoju zdążającego zarówno do zmniejszenia zużycia drewna, jak i do lepszego wykorzystania poddasza. Natomiast na rysunku poniżej przedstawiono schematy ciesielskich konstrukcji — wiązary wraz ze słupami — które zastosowano wi budynkach jednokondygnacyjnych typu halowego. Tak duża różnorodność rozwiązań konstrukcyjnych była podyktowana dążeniem budowniczych do uzyskania przekryć o możliwie największej rozpiętości.
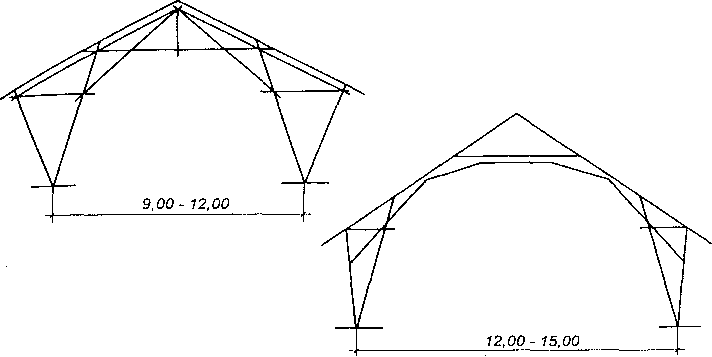 Schematy ciesielskich konstrukcji ramowych budynków halowych o rozpiętości 9,0-15,0 m.
Schematy ciesielskich konstrukcji ramowych budynków halowych o rozpiętości 9,0-15,0 m.