Stropy drewniane.
Rozróżnia się stropy: nad piwnicami, międzypiętrowe i poddasza.
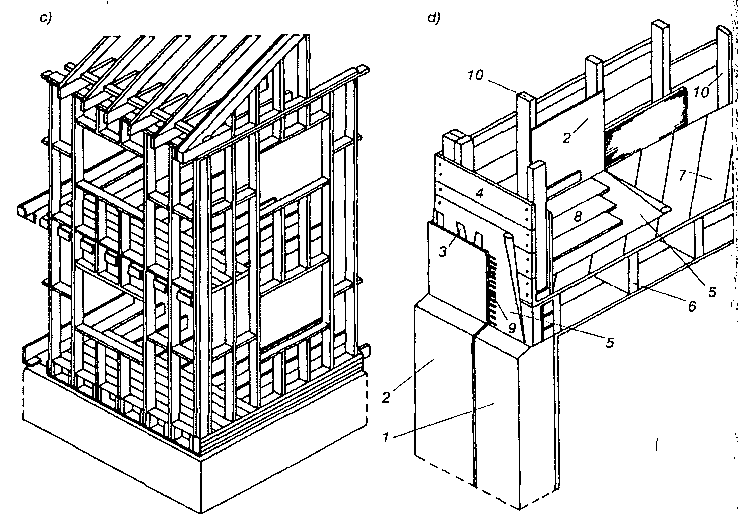
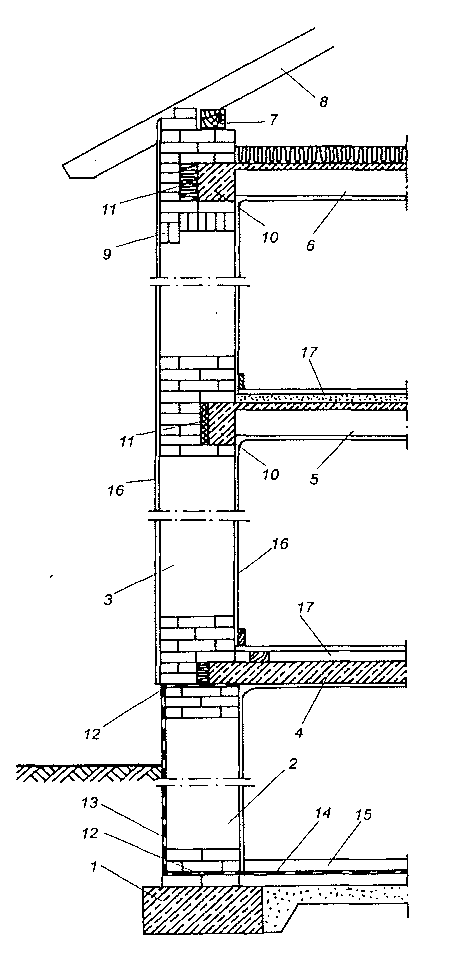
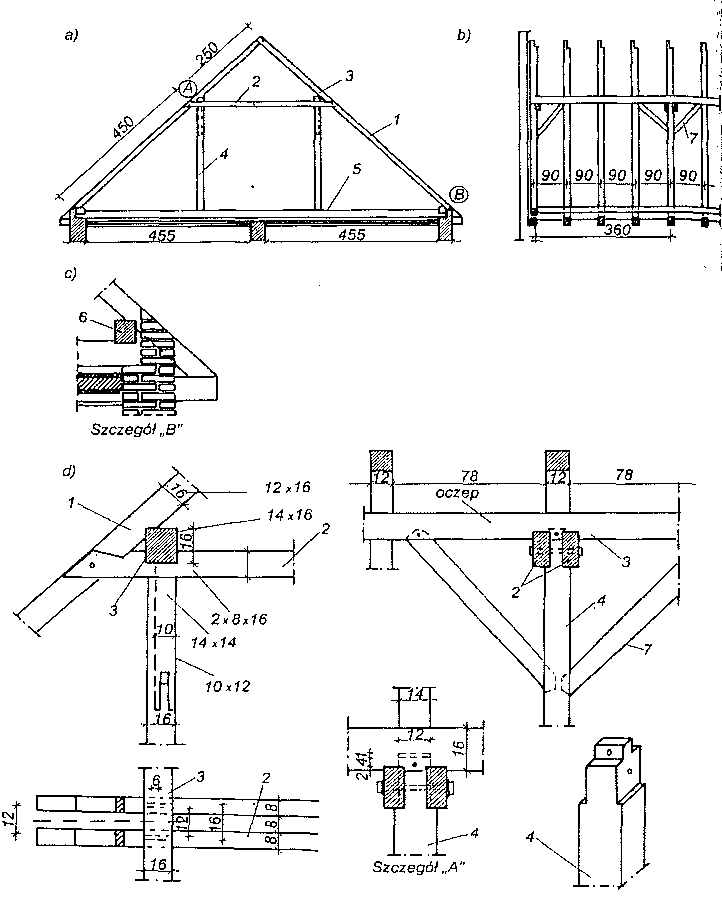
Stropy drewniane były szeroko stosowane do lat czterdziestych XX w. zarówno w budownictwie drewnianym, jak i murowanym. Ostatnio stropy te są stosowane przeważnie w budynkach drewnianych o przeznaczeniu tymczasowym i mieszkalnych jednorodzinnych. Najczęściej spotykane w budownictwie drewnianym i murowanym stropy przedstawiono na rysunku.
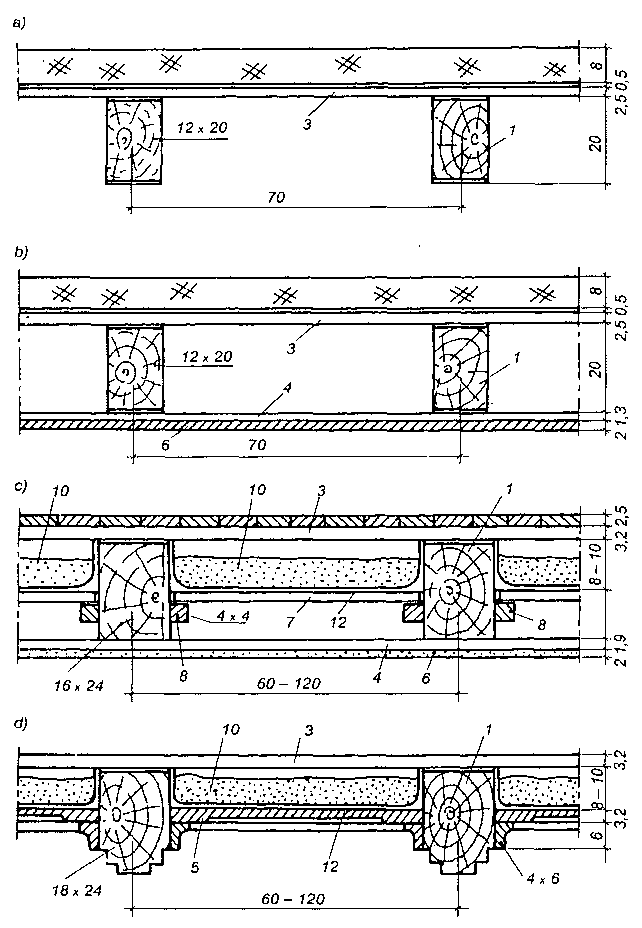
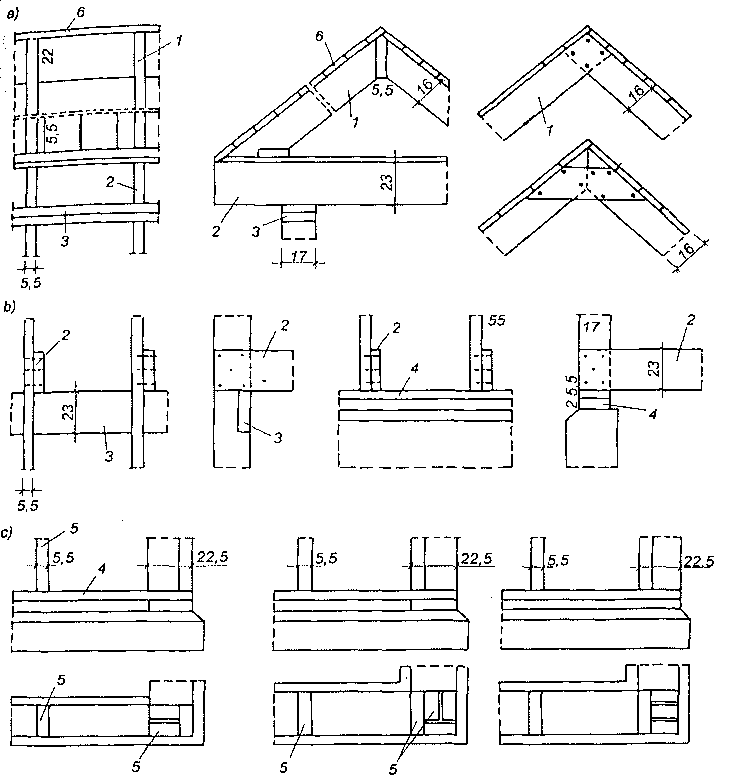
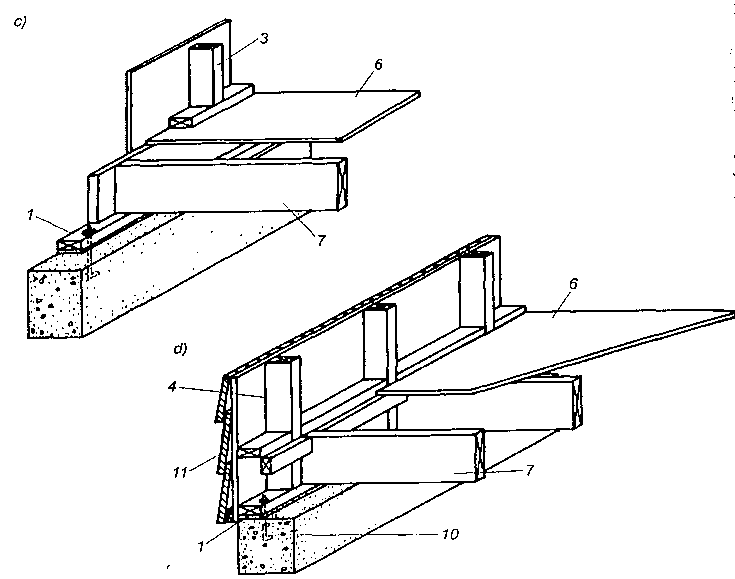
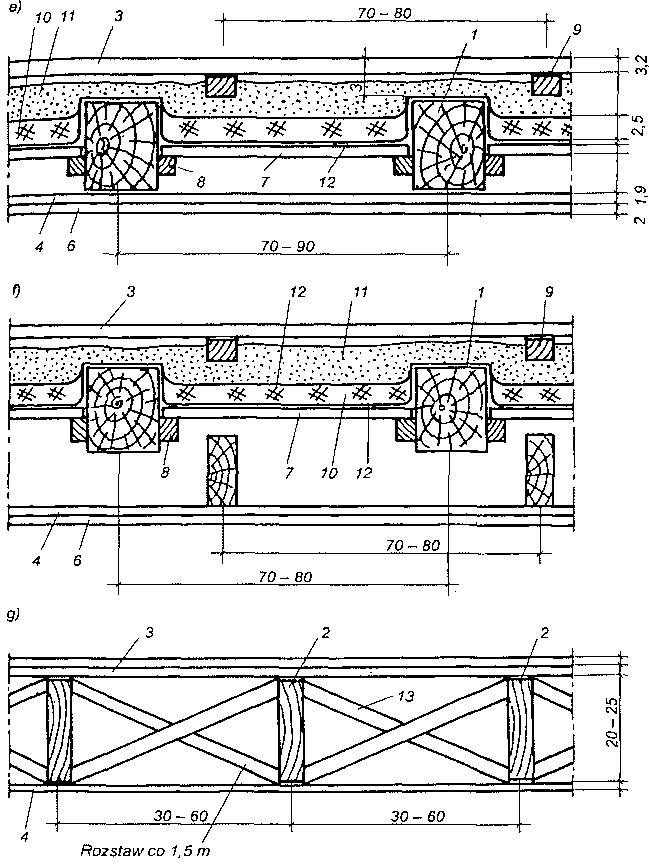 Stropy belkowe: a) strop nagi ocieplony, b) strop z podsufitką ocieplony od góry, c) strop ze ślepym pułapem, d) strop z powloką ozdobną, e) strop legarowo-listwowy, f) strop podwójny cichy, g) strop z bali usztywniony krzyżulcami; 1 — belka stropowa 12×20 do 18 x 24 cm, 2 — belki z bali 5 x 15 do 5 x 30 cm, 3 — ślepa podłoga, 4 — podsufitka z desek grub. 13-19 m lub z płyt drewnopochodnych, 5 — deski powały ozdobnej, 6 — tynk na matach z trzciny, 7 — ślepy pułap deski grubości 25 mm, 8 — listwy 40 x 40 mm, 9 — legary 50 x 70–50×90 mm, 10 — polepa, 11 — piasek, 12 — tektura smołowa lub papa, 13 — krzyżulce 25 x 70 mm.
Stropy belkowe: a) strop nagi ocieplony, b) strop z podsufitką ocieplony od góry, c) strop ze ślepym pułapem, d) strop z powloką ozdobną, e) strop legarowo-listwowy, f) strop podwójny cichy, g) strop z bali usztywniony krzyżulcami; 1 — belka stropowa 12×20 do 18 x 24 cm, 2 — belki z bali 5 x 15 do 5 x 30 cm, 3 — ślepa podłoga, 4 — podsufitka z desek grub. 13-19 m lub z płyt drewnopochodnych, 5 — deski powały ozdobnej, 6 — tynk na matach z trzciny, 7 — ślepy pułap deski grubości 25 mm, 8 — listwy 40 x 40 mm, 9 — legary 50 x 70–50×90 mm, 10 — polepa, 11 — piasek, 12 — tektura smołowa lub papa, 13 — krzyżulce 25 x 70 mm.
Najprostszym pod względem konstrukcyjnym jest strop nagi (rys. a), który jest stosowany przeważnie jako strop poddasza w budynkach mieszkalnych i gospodarskich. Do belek z wierzchu przybijane są deski o grubości 25 mm, jeśli rozstaw belek jest mniejszy od 1,0 m, lub deski o grubości 32 mm, jeśli poddasze jest użytkowane, a rozstaw belek nie jest większy od 1,20 m. Deski łączone są ze sobą na wpust i pióro, na przylgę lub na listwę.
W budynkach mieszkalnych na deskowaniu stropu układa się warstwę ocieplającą z polepy (glina mieszana z sieczką) o grubości 10-15 cm lub z płyt izolacyjnych, np. z wełny mineralnej itp. Pod polepę oraz inne warstwy ocieplające układa się na deskach papier, tekturę lub papę.
Lepszym pod względem izolacyjnym od stropu nagiego jest strop z podsufitką ocieplony od góry (rys.b). Podsufitka może być wykonana z desek struganych, jako ozdobna, lub z tynku wapienno-gipsowego na matach trzcinowych przybitych do desek. W zależności od rozstawu belek podsufitkę wykonuje się z desek o grubości 19 mm lub 25 mm.
W budynkach o kilku kondygnacjach stosuje się stropy międzypiętrowe ze ślepym pułapem i podsufitką (rys.c) lub z powałą ozdobną (rys.d). Ślepy pułap i powała ozdobna wykonywane są z desek o grubości 19 mm lub 25 mm na listwach przybitych do boku belek w połowie ich wysokości. Na ślepy pułap używane są deski gorszego gatunku niż na powałę ozdobną.
W tradycyjnych stropach ze ślepymi pułapami jako warstwę izolacyjną stosowano polepę ułożoną na papie. W nowszych rozwiązaniach zamiast ślepego pułapu i ocieplenia z polepy można stosować płyty wiórkowo-cementowe, gazobetonowe, pilśniowe lub maty z wełny mineralnej.
Strop legarowo-listwowy (rys.e) był szeroko stosowany w budownictwie tradycyjnym zarówno mieszkalnym, jak i innego przeznaczenia. W stropach tych legary układa się na podsypce z piasku lub żużla, a podłoga ślepa podniesiona jest ok. 3 cm nad górnymi powierzchniami belek stropowych. Dzięki temu drgania z podłogi nie przenoszą się bezpośrednio na belki. Belki stropowe i deski ślepego pułapu oddziela się od polepy i podsypki papą.
Strop podwójny (nazywany cichym lub szkolnym) pokazany na rys. f stosuje się do polepszenia warunków akustycznych. Strop górny jest nośny i nie różni się od stropu legarowo-listwowego, dolny zaś jest samonośny. Drgania stropu górnego nie są przekazywane na strop dolny.
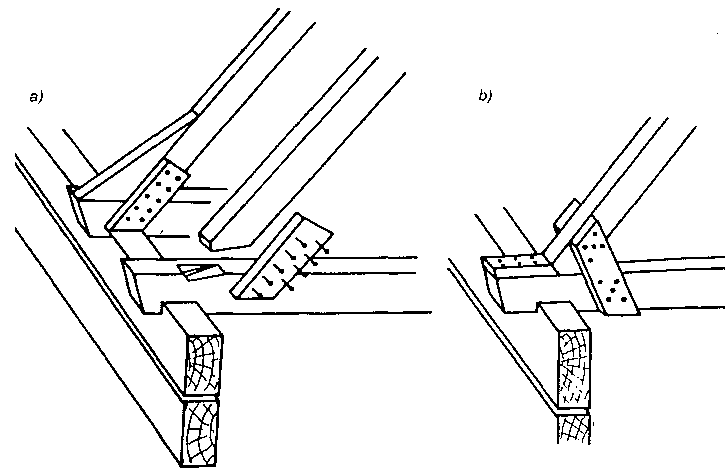
W budynkach szkieletowych wykonywanych z bali stosuje się stropy przedstawione na rys.g, które mogą być zarówno jako stropy poddasza, jak i międzypiętrowe. Belki z bali o przekroju 5×15 cm do 5 x 30 cm są ustawiane w odstępach 30-60 cm i usztywniane krzyżulcami z łat rozstawionymi co 1,5 m na długości stropu. ,
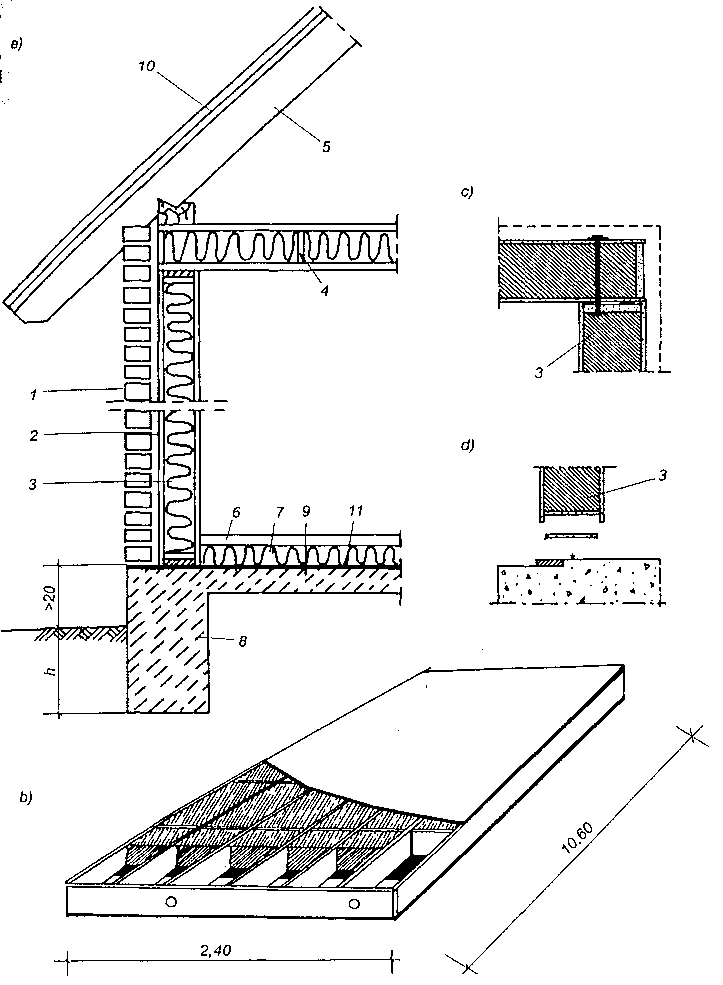
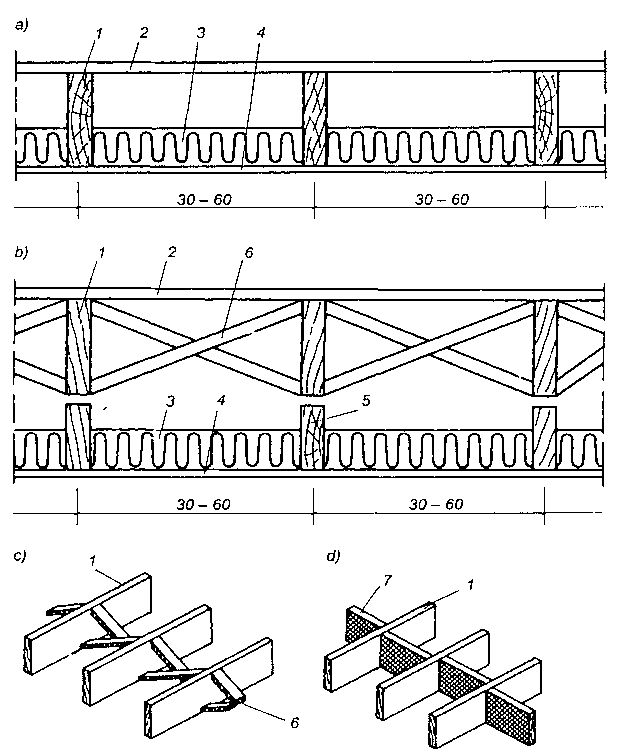 Stropy z bali: a) strop z izolacją cieplną, b) strop podwójny z izolacją cieplną, c), d) szczegóły usztywnienia belek; 1 — belka z bali 5x 15 do 5×30 cm, 2 — ślepa podłoga 7. desek, płyt drewnopochodnych lub sklejki drewnianej, 3 — izolacja z wełny mineralnej, 4 — podsufitka ognioodporna z płyt gipsowych 5 — belka stropu podwójnego 5×15 cm, 6 — krzyżulec 25 x 75 mm, 7 — deska grubości 25 mm.
Stropy z bali: a) strop z izolacją cieplną, b) strop podwójny z izolacją cieplną, c), d) szczegóły usztywnienia belek; 1 — belka z bali 5x 15 do 5×30 cm, 2 — ślepa podłoga 7. desek, płyt drewnopochodnych lub sklejki drewnianej, 3 — izolacja z wełny mineralnej, 4 — podsufitka ognioodporna z płyt gipsowych 5 — belka stropu podwójnego 5×15 cm, 6 — krzyżulec 25 x 75 mm, 7 — deska grubości 25 mm.
W starszych rozwiązaniach ślepą podłogę i podsufitkę wykonywano z desek, natomiast w nowych, jak np. typu kanadyjskiego, ślepą podłogę stanowi sklejka lub twarda płyta z materiałów drewnopochodnych, a podsufitkę stanowią płyty gipsowe mocowane do spodu belek (rys.a).
Na rysunku b przedstawiono strop podwójny (cichy) — izolację z wełny mineralnej ułożonej na podsufitce; podłoga oraz podsufitką przekazują obciążenie na dwie niezależnie od siebie pracujące belki. Strop ten stosowany jest głównie w budynkach wielorodzinnych. W domach jednorodzinnych izolacja termiczna w stropach międzypiętrowych nie jest zwykle stosowana. Jeśli jest potrzebna, to można ją ułożyć na podsufitce (rys. a).