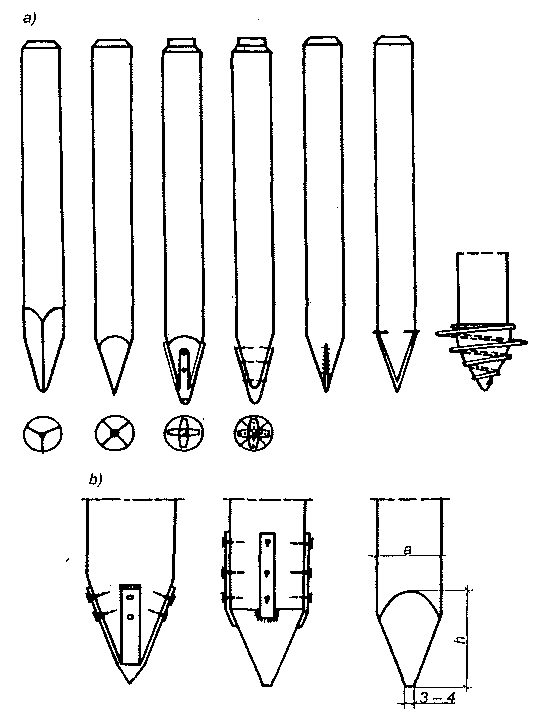
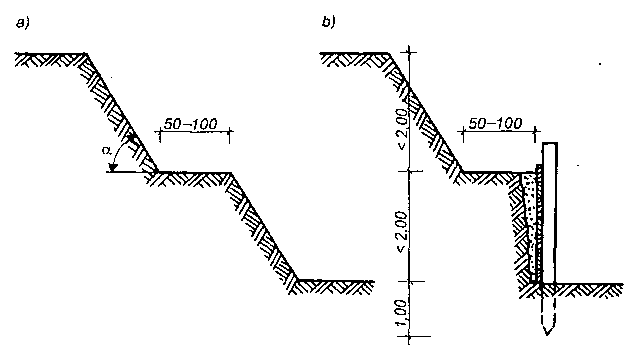
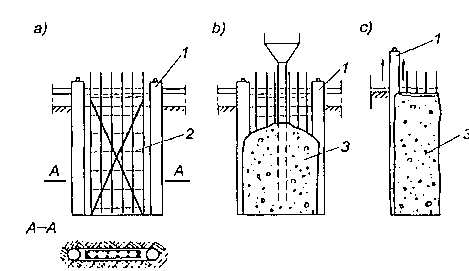
Pale prefabrykowane stosuje się zwykle przy fundamentowaniu obiektów na wodzie otwartej, gdy wystająca część pala ma pozostać zanurzona w wodzie. W takich warunkach wykonanie pali nabijanych przedstawia pewne trudności. Pale prefabrykowane wykonywane są o przekroju kwadratowym, prostokątnym, wielobocznym, okrągłym lub dwuteowym. Ponadto mogą one być o przekroju pełnym lub wydrążonym o jednolitej długości lub z odcinków. Najczęściej stosowane rodzaje pali żelbetowych przedstawiono na rysunku.
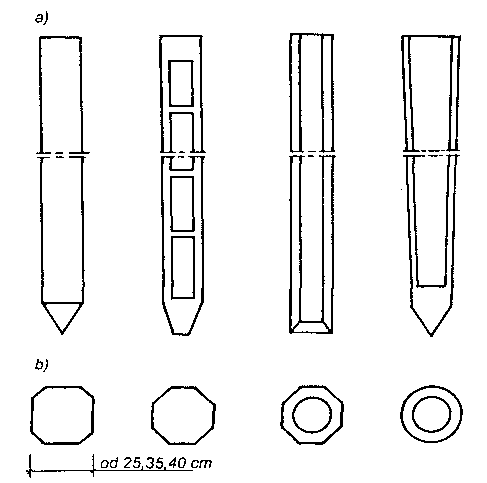 Rodzaje pali żelbetowych prefabrykowanych: a) przekroje podłużne, b) przekroje poprzeczne.
Rodzaje pali żelbetowych prefabrykowanych: a) przekroje podłużne, b) przekroje poprzeczne.
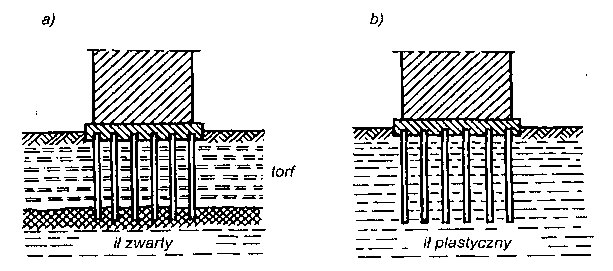
Pale wykonywane są najczęściej o pełnym przekroju kwadratowym z lekko ściętymi narożami. Pale o przekroju prostokątnym lub dwuteowym stosowane są z reguły w tych warunkach, gdy zachodzi konieczność przeniesienia momentów zginających. Zagłębia się je w grunt w taki sposób, aby płaszczyzna momentów zginających była równoległa do dłuższego boku przekroju.
Wpłukiwania pali dokonuje się za pomocą prądu wody pod ciśnieniem, dostarczanej przez odpowiednią rurę (płuczkę). Woda rozluźnia grunt w otoczeniu pala, który zagłębia się w grunt pod wpływem swego ciężaru i lekkiego tylko pobijania. Wpłukiwanie pali prądem wody powoduje rozluźnienie gruntu w otoczeniu pali i zmniejszenie ich nośności w porównaniu z palami wbijanymi.
Wwibrowania pali dokonuje się przez wibratory nasadzone na wierzch pala, które wywołują drgania pala i otaczającego go gruntu. Wskutek drgań opór gruntu znacznie zmniejsza się i pal pogrąża się pod własnym ciężarem.