O sposobie wentylowania dachu skośnego decyduje zagospodarowanie poddasza i rodzaj zastosowanych warstw wstępnego krycia
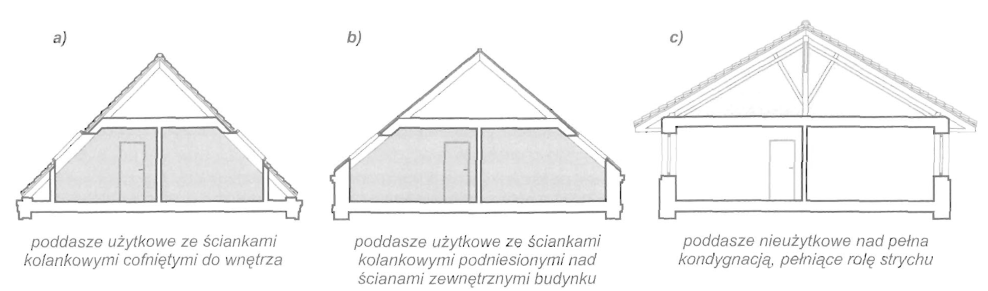
W poddaszu nieużytkowym termoizolacja umieszczona jest na stropie górnej kondygnacji. Naturalną przestrzeń wentylacyjną tworzy sama kubatura poddasza między termoizolacją a warstwą wstępnego krycia. Przestrzeń ta powinna mieć zapewniony swobodny przepływ powietrza poprzez nawiewne otwory wentylacyjne usytuowane pod okapami oraz otwory wywiewne w kalenicy dachu i w górnej części ścian szczytowych.
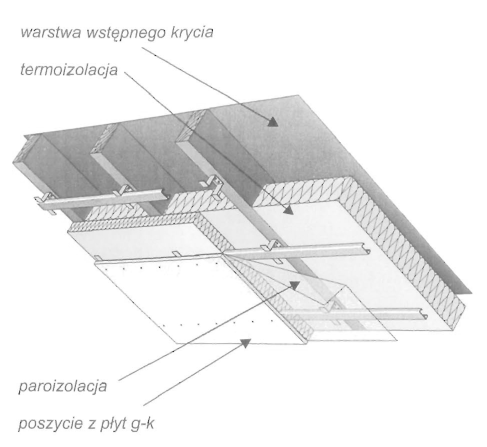
W poddaszu użytkowym wentylacja dachu ograniczona jest do szczelin wentylacyjnych umieszczonych w połaciach dachowych.
We współczesnych konstrukcjach dachowych wyróżnia się dwa podstawowe rozwiązania wentylacji połaci dachowych:
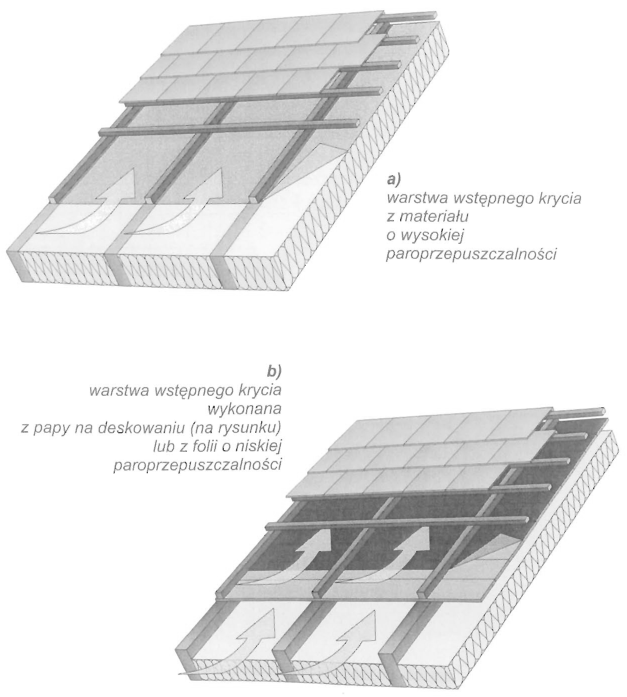
• Wentylacja dwukanałowa – Stosowana w konstrukcjach, w których warstwa wstępnego krycia wykonana jest z materiałów hydroizolacyjnych, ułożonych na deskowaniu albo z folii o niskiej paroprzepuszczalności. Dla prawidłowego działania wentylacji konieczne są dwie szczeliny wentylacyjne – pierwsza między termoizolacją a warstwą wstępnego krycia, druga między warstwą wstępnego krycia a wierzchnim pokryciem dachowym. Dolna szczelina wentylacyjna osusza izolację termiczną i konstrukcję dachu. Górna szczelina dodatkowo wzmacnia działanie szczeliny dolnej, zapewniając ponadto szybkie wysychanie wilgoci, która może się dostać pod pokrycie dachowe podczas opadów atmosferycznych połączonych z silnym wiatrem,
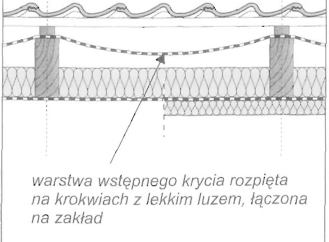
• Wentylacja jednokanałowa – Przepływająca przez połać dachu para wodna usuwana jest na zewnątrz przez powietrze przepływające w jednej szczelinie utworzonej ponad warstwą wstępnego krycia, pomiędzy kontrłatami.
Wyeliminowanie dolnej szczeliny wentylacyjnej możliwe jest tylko w przypadku zastosowania warstwy wstępnego krycia ze specjalnej wysoko paroprzepuszczaInej włókniny.
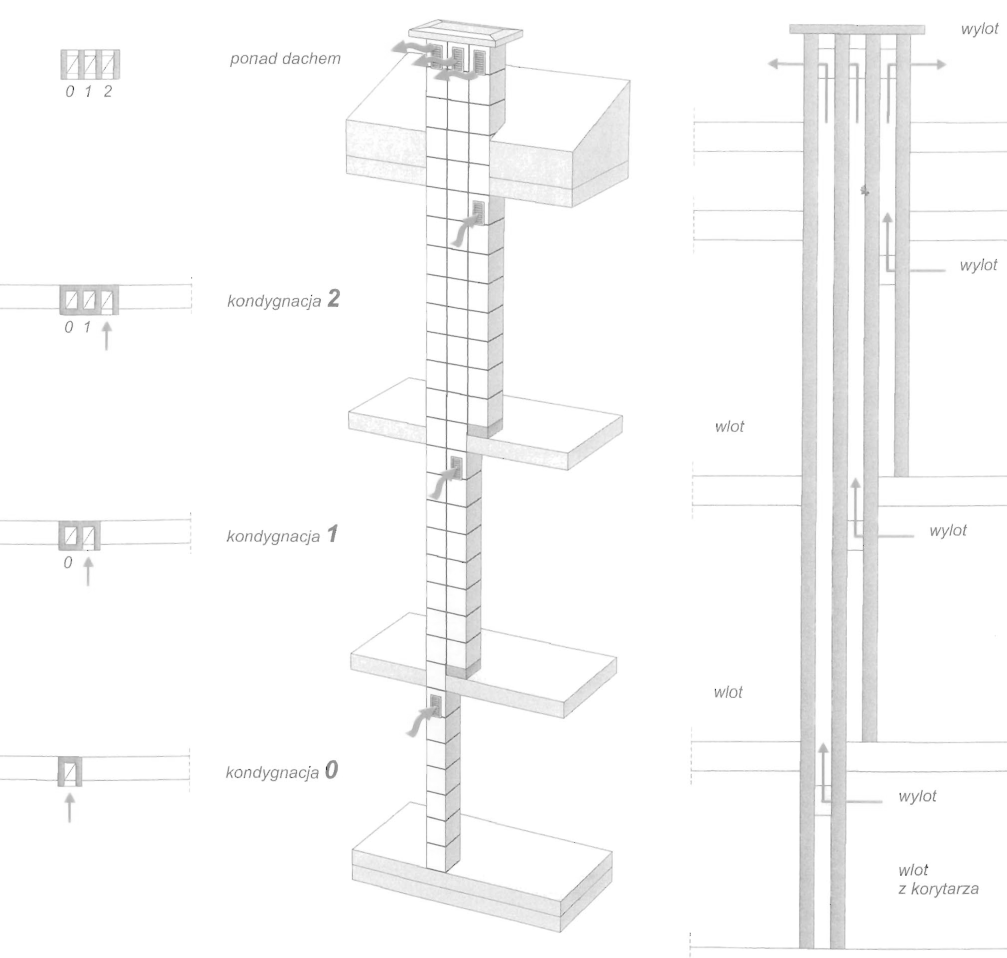
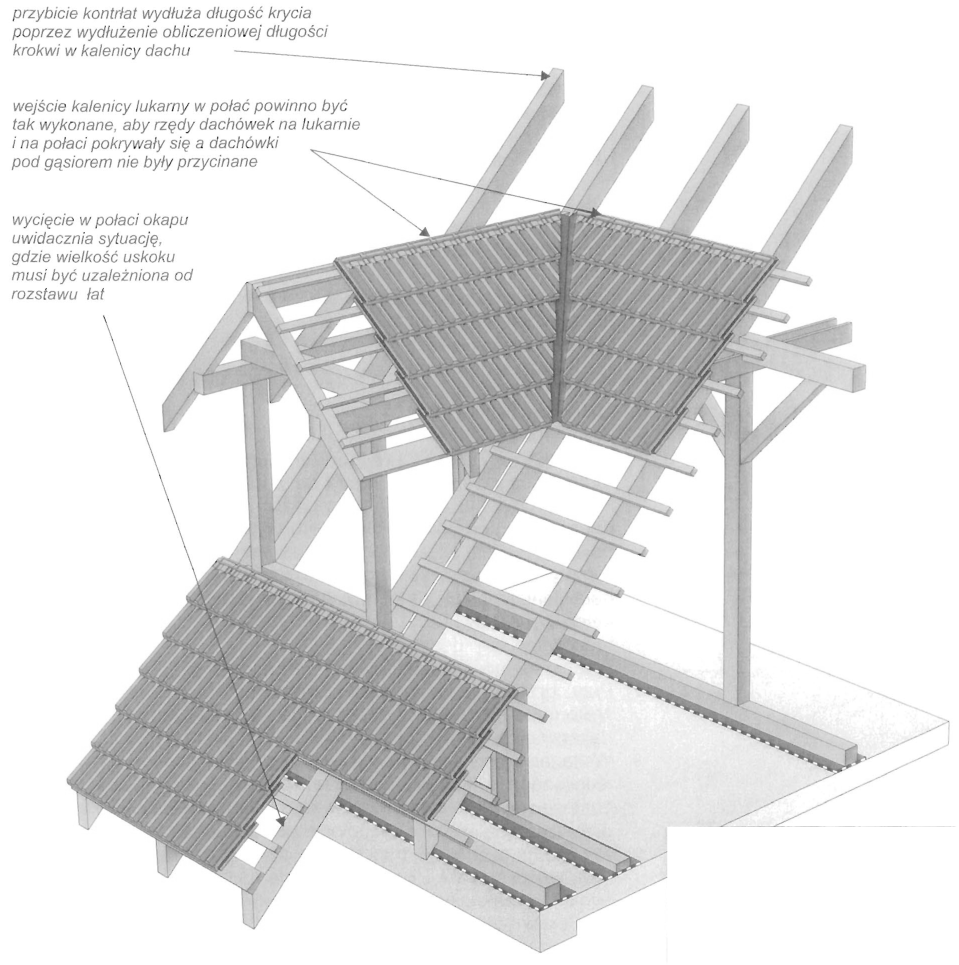
Otwory nawiewne do szczelin wentylacyjnych znajdują się pod okapem dachu. Otwory wywiewne umieszczane są w kalenicy. Wentylację liniową można dodatkowo wspomagać punktowo poprzez zastosowanie specjalnych dachówek wentylacyjnych, Zalecane jest umieszczanie dachówek wentylacyjnych w miejscach przerwania ciągłości szczeliny wentylacyjnej np. przy oknach połaciowych lub lukarnach.
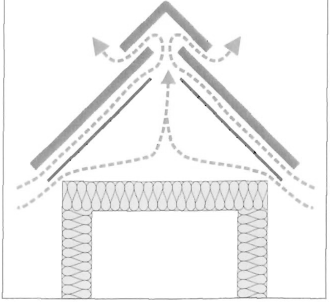 Wentylacja w poddaszu nieużytkowym -wlot powietrza przy okapie dachu, wylot w kalenicy dachu i poprzez otwory wentylacyjne w ścianach szczytowych.
Wentylacja w poddaszu nieużytkowym -wlot powietrza przy okapie dachu, wylot w kalenicy dachu i poprzez otwory wentylacyjne w ścianach szczytowych.
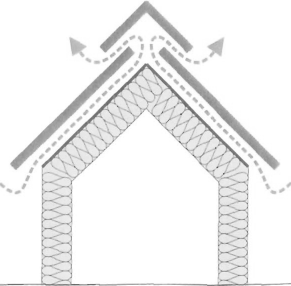 Wentylacja połaci dachowych z jedną szczeliną wentylacyjną między warstwą wstępnego krycia, a pokryciem wierzchnim, stosowana w dachach bez pełnego deskowania.
Wentylacja połaci dachowych z jedną szczeliną wentylacyjną między warstwą wstępnego krycia, a pokryciem wierzchnim, stosowana w dachach bez pełnego deskowania.
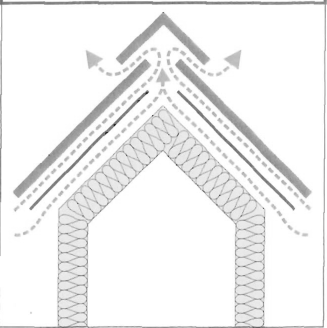 Wentylacja połaci dachowych z jedną szczeliną wentylacyjną nad termoizolacją i drugą pomiędzy sztywnym poszyciem z desek lub sklejki a pokryciem wierzchnim.
Wentylacja połaci dachowych z jedną szczeliną wentylacyjną nad termoizolacją i drugą pomiędzy sztywnym poszyciem z desek lub sklejki a pokryciem wierzchnim.